When you’re undertaking the management of temperature-sensitive pharmaceuticals, you’ll want the best devices possible. From thermometers to data loggers to more specific monitoring technology, there is a range of devices to suit your needs. Understanding how each device works and supports your cold chain management will be vitally important. These devices are effective, not just for their accurate reporting, but also because they help ensure that your valuable medical supplies are safe and that you’re correctly following all guidelines.
The Cold Chain Process
The “cold chain” refers to the process of storing and transporting vaccines or other sensitive pharmaceuticals within the safe temperature range, usually between +2°C and +8°C. Pharmaceuticals are incredibly delicate substances, and can become ineffective to patients when exposed to temperatures beyond this range. The entire cold chain process begins when your pharmaceutical is made and ends when it is administered to a client. Adhering to the cold chain process means storing your pharmaceuticals within a purpose-built form of storage, such as a medical refrigerator or transport coolers. Other industries also rely on cold chain protocols, such as electronics, agriculture, manufacturing, and food and beverage.
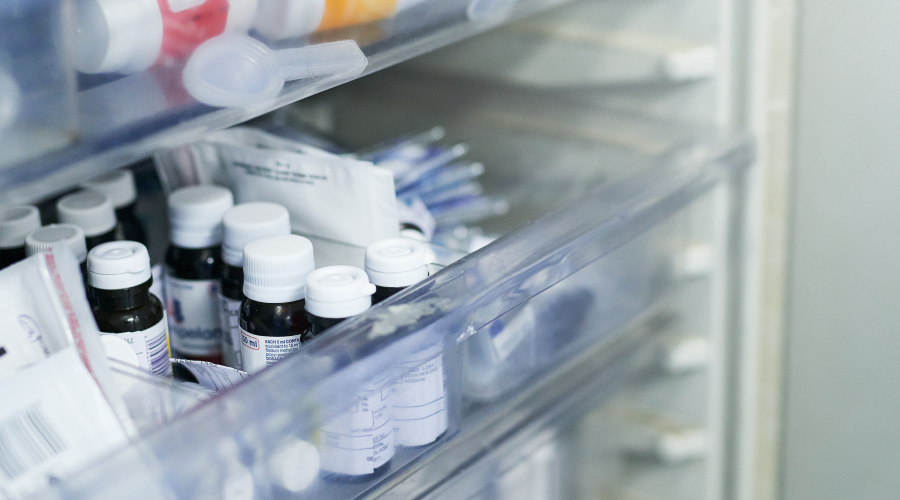
What is Cold Chain Monitoring?
During the entire cold chain process, you must be constantly monitoring and tracking temperatures. “Cold Chain Monitoring” incorporates the use of specific monitoring devices to ensure you are accurately tracking your product’s temperature. Successful cold chain monitoring will allow you to spot potential “cold chain breaches” before they occur, which is when your products move outside of their safe temperature range. It will also satisfy industry regulations. For instance, the National Vaccine Storage Guidelines dictate you must monitor the temperature of your vaccine refrigerators twice daily, or more if required.
Responsibility for cold chain monitoring should rest with a designated staff member, who will serve as the primary contact for any cold chain management issues and ensure all processes comply with regulations. Importantly, everyone involved in the journey of a temperature-sensitive product should be aware of the importance of cold chain monitoring. This includes not only logistics providers and healthcare workers, but also manufacturers who create the product and farmers who handle it at the point of harvest.
Cold Chain Temperature Monitoring Devices
An important aspect of any cold chain management system is the use of monitoring devices. These devices are designed ostensibly to report and log your storage temperature, ensuring your valuable materials remain in the cold chain. The following devices will be key for your monitoring:
Thermometers
Having a minimum/maximum thermometer is an essential device for managing your medical products. A thermometer is a temperature monitoring device equipped with sensor probes to monitor the conditions of your pharmaceuticals directly. You must choose a minimum/maximum thermometer because you will be required under regulation to manually record both minimum and maximum temperatures twice daily. When choosing a thermometer, we strongly recommend you also choose a battery-powered thermometer. This will ensure continued functionality during a power outage, making it a valuable device during emergencies.
Overall, thermometers are great because of their versatility. They can be used in a variety of situations, from monitoring blood samples in a refrigerator to an emergency cold chain breach. Although, they do lack the automation of data loggers and require manual readings twice daily as per standard regulation. The National Vaccine Storage Guidelines recommend replacing your thermometer batteries every 6-12 months and conducting annual maintenance checks.
Data loggers
Like thermometers, data loggers are used extensively throughout cold chain monitoring. They are small, electronic devices that can digitally record temperature. They are different from minimum/maximum thermometers in that they can be set to measure temperature at different time intervals. This is great for cold chain monitoring because it allows you to gather consistent data over a long period of time without the need for manual recording. We recommend setting your data loggers to record temperature at 5-minute intervals and operating at all times within the cold chain. Data loggers can be purchased as either semi-automatic or fully automatic. A semi-automatic device requires you to manually download the data onto an external device for analysis. While a fully automatic logger can continually send information to you, meaning you’ll never have to touch the device in storage.
The benefits of a data logger lie in its ability to provide information straight to your computer or even your phone via sms, which is great for stopping cold chain breaches outside of traditional work hours. Data loggers are arguably the most extensively used devices for cold chain monitoring and are incredibly versatile. Particularly when handling highly temperature-sensitive materials, such as vaccines, a data logger is highly recommended. Although, if you are looking to invest in a fully automated data logger, especially those with more advanced features, it will require higher upfront costs than a thermometer.
Wireless IoT monitoring device
Modern devices are increasingly embracing the potential of the Internet of Things (IoT). This refers to increased connectivity to the internet, with information sent directly to the network. Currently, these devices will typically come in the form of a small unit with inbuilt sensors to track conditions, in addition to an inbuilt transmitter to send your data online in real time. This is the cornerstone of an IoT – it’s always connected.
IoT devices can go one step further than traditional data loggers. Their sensors have the potential to log information on not just the temperature, but also the ambient conditions and humidity, equipment performance, and point out inaccuracies in real time. While data loggers are designed for set 5-minute intervals, an IoT monitoring device can provide real-time information, thus allowing for more proactive action in emergencies. IoT remains a growing field, with modern data loggers also incorporating aspects of this technology, particularly with its connectivity to the cloud for data analysis. As a downside, choosing IoT devices will typically require higher upfront costs. Therefore if you already have an automatic data logger with network connectivity, then investing in the benefits of an IoT system may not be worth it.
Disposable cold chain monitors
A disposable cold chain monitor is a single-use temperature indicator that can provide alerts if your product is moving beyond the cold chain. With an in-built battery, they are designed with size in mind to be incredibly portable and effective within transportation. The National Vaccine Storage Guidelines outline that these devices must be used during transport, and you should never accept vaccines that have not been accompanied by a disposable cold chain monitor. Importantly, these devices are designed to be disposable and must be discarded immediately after use. Once they record a deviation from the cold chain temperature, they have reached the end of their lifespan and must be disposed of.
Temperature chart recording system
Temperature chart recording systems are unique because they utilise a physical chart to display readings, with a visual documentation of any temperature changes. Their history dates back over a century, and they use an electromechanical device to record a temperature by drawing on a piece of paper. Because of the rise in digital technology, these paper chart recording systems are increasingly outdated and unsuitable for modern use. Therefore, if you are looking for temperature displays, this device must be used with a maximum/minimum thermometer and data loggers. Your paper chart will generally need to be replaced weekly, with your recording system lasting for approximately 12 months with one battery.
Audio and visual alarms
Alarms represent a computer control system that will alert staff to any temperature changes outside the correct range. This security device will be vitally important to pair in conjunction with your other monitoring devices, and can issue alarms to your designated staff member or to responsible workers. A back-to-base alarm is essential for any healthcare facility with highly temperature-sensitive material, such as vaccines, insulin, specific antibiotics, or injections.
Electronic freeze indicators
If you are storing material that is highly susceptible to damage from freezing, then investing in electronic freeze indicators could be a great option. These indicators have a digital display or alarm system to alert staff when their storage has moved to a freezing temperature, below 0ºC. The most common type of indicator is a freeze tag, which consists of an electronic circuit with a blinking light in the corner of the display to show it is functioning correctly. Indicators can be a great device to use in conjunction with data loggers or thermometers if your material is highly sensitive.
LED fridge display
Many modern medical refrigerators or freezers will already have a form of temperature monitoring, and it is presented as an exterior LED display. Refrigerators will use an in-built maximum/maximum thermometer to record internal temperatures. Importantly, LED displays can provide a helpful snapshot of an internal temperature but they should not be relied upon fully for cold chain monitoring. This is because their accuracy is difficult to quantify due to their in-built nature, especially in older or unserviced models. Always use these devices, alongside at least a thermometer and a data logger.
Vaccine vial monitors
Some devices are applied directly to a specific product. Vaccine Vial Monitors (VVM) are a heat-sensitive label which are attached to the outside of a vial. They are designed to indicate to staff if your vials have been affected by abnormal temperatures, with the label changing colour as an alert. The World Health Organisation (WHO) has a handy chart to help you recognise when your labels are indicating your vial is unsafe for patient use. VVM’s are great for transport situations, because they are applied directly to the vial and don’t take up extra space.
Why Are Cold Chain Monitoring Devices Important?
Investing in the right monitoring devices for your cold chain management is important for a variety of reasons:
Adhering to regulations
Depending on your facility, regulations will govern how you act. For example, vaccine practitioners must abide by the National Vaccine Storage Regulations. Under these regulations, you are required to have at a minimum a data logger and a minimum/maximum thermometer in place to continuously monitor refrigerator temperatures.
Avoiding legal issues
If your facility is found to have failed to follow the above regulations, it may face legal consequences from the Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Agency (AHPRA). Furthermore, if you administer a vaccine that has not been sufficiently monitored to a patient, you may be subject to a medical negligence claim for breaching your duty of care. This makes the use of temperature monitoring devices essential to ensuring your facility avoids legal liability.
Early detection of a cold chain breach
The effectiveness of medicine or vaccines will be dramatically reduced when exposed to temperatures outside of the cold chain. Therefore, your monitoring devices are key for identifying any potential cold chain breach before it occurs, so you can reduce the negative impacts. Particularly if an unexpected power outage were to occur.
Information for self-audit
Self-auditing is an integral part of cold chain management. Typically, you are required to undertake a self-audit at least once a year to ensure you are still compliant. A key aspect of your compliance checks will be providing information on your monitoring devices and giving up any data records you have collected. Therefore, having temperature monitoring devices that are both accurate and consistent will ensure you are best positioned to complete the self-audit smoothly.
Remote access monitoring
The ability of your devices to provide real-time information remotely will be highly beneficial for your cold chain management. This reduces the need to open your refrigerator or freezer door for regular physical checks or inspections, thus reducing the amount of damaging hot air from entering.
Checking your refrigerator’s condition
If your monitoring devices are recording regular fluctuations in temperature or inconsistent performance, then it could mean your refrigerator needs maintenance. We recommend that you service your medical refrigerator at least once a year; this rationale also applies to vaccine storage units, ultra-low freezers, or pharmacy refrigerators, among others.
Cost saving
Vaccines and other medical substances are valuable materials that can be costly for facilities to dispose of. If you put in place the correct monitoring devices, you not only reduce your waste but can also save your facility expensive recalls and transit costs.

Common Mistakes to Avoid
To ensure you are getting the most out of your monitoring devices, it is important to be aware of potential mistakes and how you can avoid them:
Using non-certified devices
Devices that have not been properly calibrated or certified can potentially provide inaccurate data. For instance, your thermometers are required to be HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) approved for use. This will ensure accuracy and reliability, because HACCP-approved thermometers must be accurate to at least within 1°C, and be robust enough to withstand consistent use.
Human error
When temperature monitoring is done manually, there is always a risk of human error, which can lead to inaccurate readings. Staff may make mistakes due to lapses in attention, incorrect monitoring techniques, or insufficient training. Because monitoring the cold chain process is critical to ensuring product safety, relying solely on manual methods can be risky.
Failing to set up the device correctly
The initial setup phase for a new device will be critical for its effectiveness. You should ensure all steps followed before use are carried out accurately. For instance, the alert function on data loggers generally has to be manually activated in the setup phase for them to work.
Incorrect placement of the device
When placing a device within the cold chain, choosing the best position can make or break your monitoring. Placing a thermometer near the door or against the side could make it more sensitive to door openings and affect its ability to give accurate readings. Generally, we recommend that all devices placed within a medical refrigerator be as close to the middle. If your sensitive materials are being transported, we recommend placing them as close to the centre of your products as possible. Obviously, the exact position of your device will greatly depend on its unique characteristics; you should refer to your device manufacturer or state and territory health departments for further assistance.
Failing to consider storage conditions
Many of the devices you are operating will not be able to withstand all conditions. This is particularly relevant when you are using a ULT (Ultra-Low Temperature) freezer, which can reach temperatures as low as -90°C. Disposable cold chain monitors are generally designed for just the cold chain temperature range, and would be unsuitable for a ULT freezer’s extreme lows. To ensure you avoid this mistake, utilising devices that can withstand these extreme storage conditions will be key.
Failing to carry out regular calibration checks
Just like any piece of equipment, your devices may become less effective over time. Regulations will dictate that you conduct regular checks on your devices annually. For instance, a thermometer in a medical refrigerator must be checked at least once a year. The “slush test” is an accuracy test recommended by the National Vaccine Storage Guidelines. The test involves the following steps:
- Fill a polystyrene or plastic cup with cold water.
- Place the cup in the refrigerator freezer until a fine layer of ice forms on the top and small sections of ice form within the fluid (this may take up to 2 1⁄2 hours). The presence of ice is an indication that the temperature of the water has reached 0°C.
- Place the temperature probe into the middle of the container (be careful not to let the probe touch the container).
- Observe the temperature on the display screen after 2 minutes.
- Document the date of the accuracy check.
Each of your devices will have different accuracy checks. As always, if you are unsure, please refer to your designated staff member or contact your state and territory health departments.
Insufficient Cold Chain Management training
Unique situations will always present themselves in cold chain management, and all staff members must be properly trained to avoid any of the aforementioned mistakes. Your healthcare facility is directly responsible for training all staff members under cold chain protocol, with support from your state and territory health departments. Training is typically delivered through online modules provided by the relevant health authority. Based on the National Vaccine Storage Vaccine Guidelines, these modules cover the essential aspects of the cold chain. Including the use of temperature monitoring equipment and how to identify and report a suspected cold chain breach.
Monitoring devices are a central aspect of all cold chain management. Understanding each device, the reasons why they are important, and how to avoid potential mistakes will allow you to be best prepared to help patients moving forward. For more information on medical cold storage products, please contact the friendly team at Vacc-Safe.



